</pre>
<pre>#include "stdafx.h"
#include "tripod.h"
#include "tripodDlg.h"
#include "LVServerDefs.h"
#include "math.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define new DEBUG_NEW
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[] = __FILE__;
#endif
using namespace std;
class CAboutDlg : public CDialog
{
public:
CAboutDlg();
enum { IDD = IDD_ABOUTBOX };
protected:
virtual void DoDataExchange(CDataExchange* pDX);
protected:
DECLARE_MESSAGE_MAP()
};
CAboutDlg::CAboutDlg() : CDialog(CAboutDlg::IDD)
{
}
void CAboutDlg::DoDataExchange(CDataExchange* pDX)
{
CDialog::DoDataExchange(pDX);
}
BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP(CAboutDlg, CDialog)
END_MESSAGE_MAP()
CTripodDlg::CTripodDlg(CWnd* pParent )
: CDialog(CTripodDlg::IDD, pParent)
{
m_hIcon = AfxGetApp()->LoadIcon(IDR_MAINFRAME);
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader = NULL;
}
static unsigned PixelBytes(int w, int bpp)
{
return (w * bpp + 7) / 8;
}
static unsigned DibRowSize(int w, int bpp)
{
return (w * bpp + 31) / 32 * 4;
}
static unsigned DibRowSize(LPBITMAPINFOHEADER pbi)
{
return DibRowSize(pbi->biWidth, pbi->biBitCount);
}
static unsigned DibRowPadding(int w, int bpp)
{
return DibRowSize(w, bpp) - PixelBytes(w, bpp);
}
static unsigned DibRowPadding(LPBITMAPINFOHEADER pbi)
{
return DibRowPadding(pbi->biWidth, pbi->biBitCount);
}
static unsigned DibImageSize(int w, int h, int bpp)
{
return h * DibRowSize(w, bpp);
}
static size_t DibSize(int w, int h, int bpp)
{
return sizeof (BITMAPINFOHEADER) + DibImageSize(w, h, bpp);
}
void CTripodDlg::DoDataExchange(CDataExchange* pDX)
{
CDialog::DoDataExchange(pDX);
DDX_Control(pDX, IDC_PROCESSEDVIEW, m_cVideoProcessedView);
DDX_Control(pDX, IDC_UNPROCESSEDVIEW, m_cVideoUnprocessedView);
}
BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP(CTripodDlg, CDialog)
ON_WM_SYSCOMMAND()
ON_WM_PAINT()
ON_WM_QUERYDRAGICON()
ON_BN_CLICKED(IDEXIT, OnExit)
END_MESSAGE_MAP()
BOOL CTripodDlg::OnInitDialog()
{
CDialog::OnInitDialog();
ASSERT((IDM_ABOUTBOX & 0xFFF0) == IDM_ABOUTBOX);
ASSERT(IDM_ABOUTBOX < 0xF000);
CMenu* pSysMenu = GetSystemMenu(FALSE);
if (pSysMenu != NULL)
{
CString strAboutMenu;
strAboutMenu.LoadString(IDS_ABOUTBOX);
if (!strAboutMenu.IsEmpty())
{
pSysMenu->AppendMenu(MF_SEPARATOR);
pSysMenu->AppendMenu(MF_STRING, IDM_ABOUTBOX, strAboutMenu);
}
}
SetIcon(m_hIcon, TRUE);
SetIcon(m_hIcon, FALSE);
char sRegUnprocessedView[] = "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\Software\\UnprocessedView";
m_cVideoUnprocessedView.PrepareControl("UnprocessedView", sRegUnprocessedView, 0 );
m_cVideoUnprocessedView.EnableUIElements(UIELEMENT_STATUSBAR,0,TRUE);
m_cVideoUnprocessedView.ConnectCamera2();
m_cVideoUnprocessedView.SetEnablePreview(TRUE);
char sRegProcessedView[] = "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\Software\\ProcessedView";
m_cVideoProcessedView.PrepareControl("ProcessedView", sRegProcessedView, 0 );
m_cVideoProcessedView.EnableUIElements(UIELEMENT_STATUSBAR,0,TRUE);
m_cVideoProcessedView.ConnectCamera2();
m_cVideoProcessedView.SetEnablePreview(TRUE);
m_cVideoProcessedView.SetPreviewMaxHeight(240);
m_cVideoProcessedView.SetPreviewMaxWidth(320);
m_cVideoProcessedView.GetWindowRect(m_rectForProcessedView);
ScreenToClient(m_rectForProcessedView);
allocateDib(CSize(320, 240));
m_cVideoProcessedView.StartVideoHook(0);
return TRUE;
}
void CTripodDlg::OnSysCommand(UINT nID, LPARAM lParam)
{
if ((nID & 0xFFF0) == IDM_ABOUTBOX)
{
CAboutDlg dlgAbout;
dlgAbout.DoModal();
}
else
{
CDialog::OnSysCommand(nID, lParam);
}
}
void CTripodDlg::OnPaint()
{
if (IsIconic())
{
CPaintDC dc(this);
SendMessage(WM_ICONERASEBKGND, (WPARAM) dc.GetSafeHdc(), 0);
int cxIcon = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXICON);
int cyIcon = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYICON);
CRect rect;
GetClientRect(&rect);
int x = (rect.Width() - cxIcon + 1) / 2;
int y = (rect.Height() - cyIcon + 1) / 2;
dc.DrawIcon(x, y, m_hIcon);
}
else
{
CDialog::OnPaint();
}
}
HCURSOR CTripodDlg::OnQueryDragIcon()
{
return (HCURSOR) m_hIcon;
}
void CTripodDlg::OnExit()
{
m_cVideoUnprocessedView.StopVideoHook(0);
m_cVideoUnprocessedView.DisconnectCamera();
m_cVideoProcessedView.StopVideoHook(0);
m_cVideoProcessedView.DisconnectCamera();
DestroyWindow();
}
BEGIN_EVENTSINK_MAP(CTripodDlg, CDialog)
ON_EVENT(CTripodDlg, IDC_PROCESSEDVIEW, 1 , OnPortalNotificationProcessedview, VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_I4)
END_EVENTSINK_MAP()
void CTripodDlg::OnPortalNotificationProcessedview(long lMsg, long lParam1, long lParam2, long lParam3)
{
#define NOTIFICATIONMSG_VIDEOHOOK 10
LPBITMAPINFOHEADER lpBitmapInfoHeader;
LPBYTE lpBitmapPixelData;
unsigned long lTimeStamp;
switch(lMsg) {
case NOTIFICATIONMSG_VIDEOHOOK:
{
lpBitmapInfoHeader = (LPBITMAPINFOHEADER) lParam1;
lpBitmapPixelData = (LPBYTE) lParam2;
lTimeStamp = (unsigned long) lParam3;
grayScaleTheFrameData(lpBitmapInfoHeader, lpBitmapPixelData);
doMyImageProcessing(lpBitmapInfoHeader);
displayMyResults(lpBitmapInfoHeader);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void CTripodDlg::allocateDib(CSize sz)
{
if(m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader) {
free(m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader);
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader = NULL;
}
if(sz.cx | sz.cy) {
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader = (LPBITMAPINFOHEADER)malloc(DibSize(sz.cx, sz.cy, 24));
ASSERT(m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader);
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biSize = sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER);
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biWidth = sz.cx;
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biHeight = sz.cy;
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biPlanes = 1;
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biBitCount = 24;
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biCompression = 0;
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biSizeImage = DibImageSize(sz.cx, sz.cy, 24);
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biXPelsPerMeter = 0;
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biYPelsPerMeter = 0;
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biClrImportant = 0;
m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader->biClrUsed = 0;
}
}
void CTripodDlg::displayMyResults(LPBITMAPINFOHEADER lpThisBitmapInfoHeader)
{
CDC *pDC;
pDC = GetDC();
int nOldMode = SetStretchBltMode(pDC->GetSafeHdc(),COLORONCOLOR);
StretchDIBits(
pDC->GetSafeHdc(),
m_rectForProcessedView.left,
m_rectForProcessedView.top,
m_rectForProcessedView.Width(),
m_rectForProcessedView.Height(),
0,
0,
lpThisBitmapInfoHeader->biWidth,
lpThisBitmapInfoHeader->biHeight,
m_destinationBmp,
(BITMAPINFO*)m_destinationBitmapInfoHeader,
DIB_RGB_COLORS,
SRCCOPY
);
SetStretchBltMode(pDC->GetSafeHdc(),nOldMode);
ReleaseDC(pDC);
free(m_destinationBmp);
}
void CTripodDlg::grayScaleTheFrameData(LPBITMAPINFOHEADER lpThisBitmapInfoHeader, LPBYTE lpThisBitmapPixelData)
{
unsigned int W, H;
BYTE *sourceBmp;
unsigned int row, col;
unsigned long i;
BYTE grayValue;
BYTE redValue;
BYTE greenValue;
BYTE blueValue;
W = lpThisBitmapInfoHeader->biWidth;
H = lpThisBitmapInfoHeader->biHeight;
m_destinationBmp = (BYTE*)malloc(H*3*W*sizeof(BYTE));
sourceBmp = lpThisBitmapPixelData;
for (row = 0; row < H; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < W; col++) {
i = (unsigned long)(row*3*W + 3*col);
blueValue = *(sourceBmp + i);
greenValue = *(sourceBmp + i + 1);
redValue = *(sourceBmp + i + 2);
grayValue = (BYTE)(0.299*redValue + 0.587*greenValue + 0.114*blueValue);
*(m_destinationBmp + i) = grayValue;
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 1) = grayValue;
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 2) = grayValue;
}
}
}
void CTripodDlg::doMyImageProcessing(LPBITMAPINFOHEADER lpThisBitmapInfoHeader)
{
unsigned int W, H;
unsigned int row, col;
unsigned long i;
int upperThreshold = 60;
int lowerThreshold = 30;
unsigned long iOffset;
int rowOffset;
int colOffset;
int rowTotal = 0;
int colTotal = 0;
int Gx;
int Gy;
float thisAngle;
int newAngle;
bool edgeEnd;
int GxMask[3][3];
int GyMask[3][3];
int newPixel;
int gaussianMask[5][5];
W = lpThisBitmapInfoHeader->biWidth;
H = lpThisBitmapInfoHeader->biHeight;
for (row = 0; row < H; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < W; col++) {
edgeDir[row][col] = 0;
}
}
GxMask[0][0] = -1; GxMask[0][1] = 0; GxMask[0][2] = 1;
GxMask[1][0] = -2; GxMask[1][1] = 0; GxMask[1][2] = 2;
GxMask[2][0] = -1; GxMask[2][1] = 0; GxMask[2][2] = 1;
GyMask[0][0] = 1; GyMask[0][1] = 2; GyMask[0][2] = 1;
GyMask[1][0] = 0; GyMask[1][1] = 0; GyMask[1][2] = 0;
GyMask[2][0] = -1; GyMask[2][1] = -2; GyMask[2][2] = -1;
gaussianMask[0][0] = 2; gaussianMask[0][1] = 4; gaussianMask[0][2] = 5; gaussianMask[0][3] = 4; gaussianMask[0][4] = 2;
gaussianMask[1][0] = 4; gaussianMask[1][1] = 9; gaussianMask[1][2] = 12; gaussianMask[1][3] = 9; gaussianMask[1][4] = 4;
gaussianMask[2][0] = 5; gaussianMask[2][1] = 12; gaussianMask[2][2] = 15; gaussianMask[2][3] = 12; gaussianMask[2][4] = 2;
gaussianMask[3][0] = 4; gaussianMask[3][1] = 9; gaussianMask[3][2] = 12; gaussianMask[3][3] = 9; gaussianMask[3][4] = 4;
gaussianMask[4][0] = 2; gaussianMask[4][1] = 4; gaussianMask[4][2] = 5; gaussianMask[4][3] = 4; gaussianMask[4][4] = 2;
for (row = 2; row < H-2; row++) {
for (col = 2; col < W-2; col++) {
newPixel = 0;
for (rowOffset=-2; rowOffset<=2; rowOffset++) {
for (colOffset=-2; colOffset<=2; colOffset++) {
rowTotal = row + rowOffset;
colTotal = col + colOffset;
iOffset = (unsigned long)(rowTotal*3*W + colTotal*3);
newPixel += (*(m_destinationBmp + iOffset)) * gaussianMask[2 + rowOffset][2 + colOffset];
}
}
i = (unsigned long)(row*3*W + col*3);
*(m_destinationBmp + i) = newPixel / 159;
}
}
for (row = 1; row < H-1; row++) {
for (col = 1; col < W-1; col++) {
i = (unsigned long)(row*3*W + 3*col);
Gx = 0;
Gy = 0;
for (rowOffset=-1; rowOffset<=1; rowOffset++) {
for (colOffset=-1; colOffset<=1; colOffset++) {
rowTotal = row + rowOffset;
colTotal = col + colOffset;
iOffset = (unsigned long)(rowTotal*3*W + colTotal*3);
Gx = Gx + (*(m_destinationBmp + iOffset) * GxMask[rowOffset + 1][colOffset + 1]);
Gy = Gy + (*(m_destinationBmp + iOffset) * GyMask[rowOffset + 1][colOffset + 1]);
}
}
gradient[row][col] = sqrt(pow(Gx,2.0) + pow(Gy,2.0));
thisAngle = (atan2(Gx,Gy)/3.14159) * 180.0;
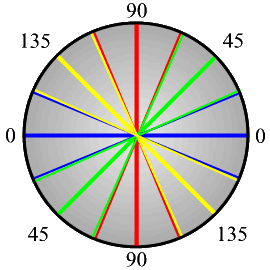
if ( ( (thisAngle < 22.5) && (thisAngle > -22.5) ) || (thisAngle > 157.5) || (thisAngle < -157.5) )
newAngle = 0;
if ( ( (thisAngle > 22.5) && (thisAngle < 67.5) ) || ( (thisAngle < -112.5) && (thisAngle > -157.5) ) )
newAngle = 45;
if ( ( (thisAngle > 67.5) && (thisAngle < 112.5) ) || ( (thisAngle < -67.5) && (thisAngle > -112.5) ) )
newAngle = 90;
if ( ( (thisAngle > 112.5) && (thisAngle < 157.5) ) || ( (thisAngle < -22.5) && (thisAngle > -67.5) ) )
newAngle = 135;
edgeDir[row][col] = newAngle;
}
}
for (row = 1; row < H - 1; row++) {
for (col = 1; col < W - 1; col++) {
edgeEnd = false;
if (gradient[row][col] > upperThreshold) {
switch (edgeDir[row][col]){
case 0:
findEdge(0, 1, row, col, 0, lowerThreshold);
break;
case 45:
findEdge(1, 1, row, col, 45, lowerThreshold);
break;
case 90:
findEdge(1, 0, row, col, 90, lowerThreshold);
break;
case 135:
findEdge(1, -1, row, col, 135, lowerThreshold);
break;
default :
i = (unsigned long)(row*3*W + 3*col);
*(m_destinationBmp + i) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 1) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 2) = 0;
break;
}
}
else {
i = (unsigned long)(row*3*W + 3*col);
*(m_destinationBmp + i) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 1) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 2) = 0;
}
}
}
for (row = 0; row < H; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < W; col++) {
i = (unsigned long)(row*3*W + 3*col);
if( ((*(m_destinationBmp + i) != 255) && (*(m_destinationBmp + i) != 0)) || ((*(m_destinationBmp + i + 1) != 255) && (*(m_destinationBmp + i + 1) != 0)) || ((*(m_destinationBmp + i + 2) != 255) && (*(m_destinationBmp + i + 2) != 0)) )
*(m_destinationBmp + i) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 1) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 2) = 0;
}
}
for (row = 1; row < H - 1; row++) {
for (col = 1; col < W - 1; col++) {
i = (unsigned long)(row*3*W + 3*col);
if (*(m_destinationBmp + i) == 255) {
switch (edgeDir[row][col]) {
case 0:
suppressNonMax( 1, 0, row, col, 0, lowerThreshold);
break;
case 45:
suppressNonMax( 1, -1, row, col, 45, lowerThreshold);
break;
case 90:
suppressNonMax( 0, 1, row, col, 90, lowerThreshold);
break;
case 135:
suppressNonMax( 1, 1, row, col, 135, lowerThreshold);
break;
default :
break;
}
}
}
}
}
void CTripodDlg::findEdge(int rowShift, int colShift, int row, int col, int dir, int lowerThreshold)
{
int W = 320;
int H = 240;
int newRow;
int newCol;
unsigned long i;
bool edgeEnd = false;
if (colShift < 0) {
if (col > 0)
newCol = col + colShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (col < W - 1) {
newCol = col + colShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
if (rowShift < 0) {
if (row > 0)
newRow = row + rowShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (row < H - 1) {
newRow = row + rowShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
while ( (edgeDir[newRow][newCol]==dir) && !edgeEnd && (gradient[newRow][newCol] > lowerThreshold) ) {
i = (unsigned long)(newRow*3*W + 3*newCol);
*(m_destinationBmp + i) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 1) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 2) = 255;
if (colShift < 0) {
if (newCol > 0)
newCol = newCol + colShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (newCol < W - 1) {
newCol = newCol + colShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
if (rowShift < 0) {
if (newRow > 0)
newRow = newRow + rowShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (newRow < H - 1) {
newRow = newRow + rowShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
}
}
void CTripodDlg::suppressNonMax(int rowShift, int colShift, int row, int col, int dir, int lowerThreshold)
{
int W = 320;
int H = 240;
int newRow = 0;
int newCol = 0;
unsigned long i;
bool edgeEnd = false;
float nonMax[320][3];
int pixelCount = 0;
int count;
int max[3];
if (colShift < 0) {
if (col > 0)
newCol = col + colShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (col < W - 1) {
newCol = col + colShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
if (rowShift < 0) {
if (row > 0)
newRow = row + rowShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (row < H - 1) {
newRow = row + rowShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
i = (unsigned long)(newRow*3*W + 3*newCol);
while ((edgeDir[newRow][newCol] == dir) && !edgeEnd && (*(m_destinationBmp + i) == 255)) {
if (colShift < 0) {
if (newCol > 0)
newCol = newCol + colShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (newCol < W - 1) {
newCol = newCol + colShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
if (rowShift < 0) {
if (newRow > 0)
newRow = newRow + rowShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (newRow < H - 1) {
newRow = newRow + rowShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
nonMax[pixelCount][0] = newRow;
nonMax[pixelCount][1] = newCol;
nonMax[pixelCount][2] = gradient[newRow][newCol];
pixelCount++;
i = (unsigned long)(newRow*3*W + 3*newCol);
}
edgeEnd = false;
colShift *= -1;
rowShift *= -1;
if (colShift < 0) {
if (col > 0)
newCol = col + colShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (col < W - 1) {
newCol = col + colShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
if (rowShift < 0) {
if (row > 0)
newRow = row + rowShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (row < H - 1) {
newRow = row + rowShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
i = (unsigned long)(newRow*3*W + 3*newCol);
while ((edgeDir[newRow][newCol] == dir) && !edgeEnd && (*(m_destinationBmp + i) == 255)) {
if (colShift < 0) {
if (newCol > 0)
newCol = newCol + colShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (newCol < W - 1) {
newCol = newCol + colShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
if (rowShift < 0) {
if (newRow > 0)
newRow = newRow + rowShift;
else
edgeEnd = true;
} else if (newRow < H - 1) {
newRow = newRow + rowShift;
} else
edgeEnd = true;
nonMax[pixelCount][0] = newRow;
nonMax[pixelCount][1] = newCol;
nonMax[pixelCount][2] = gradient[newRow][newCol];
pixelCount++;
i = (unsigned long)(newRow*3*W + 3*newCol);
}
max[0] = 0;
max[1] = 0;
max[2] = 0;
for (count = 0; count < pixelCount; count++) {
if (nonMax[count][2] > max[2]) {
max[0] = nonMax[count][0];
max[1] = nonMax[count][1];
max[2] = nonMax[count][2];
}
}
for (count = 0; count < pixelCount; count++) {
i = (unsigned long)(nonMax[count][0]*3*W + 3*nonMax[count][1]);
*(m_destinationBmp + i) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 1) =
*(m_destinationBmp + i + 2) = 0;
}
}